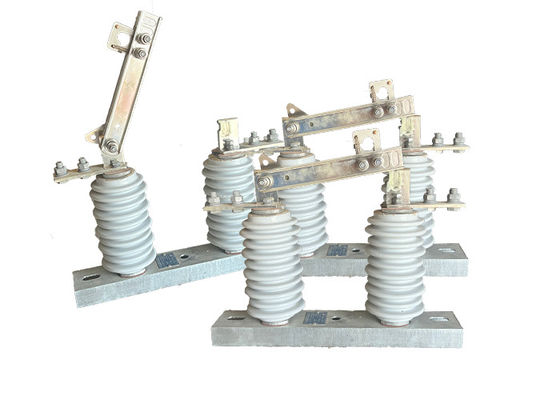
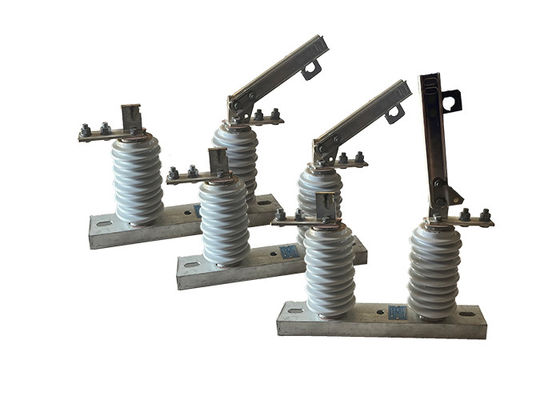
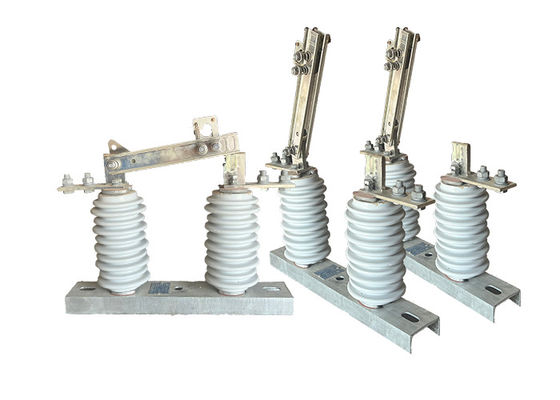
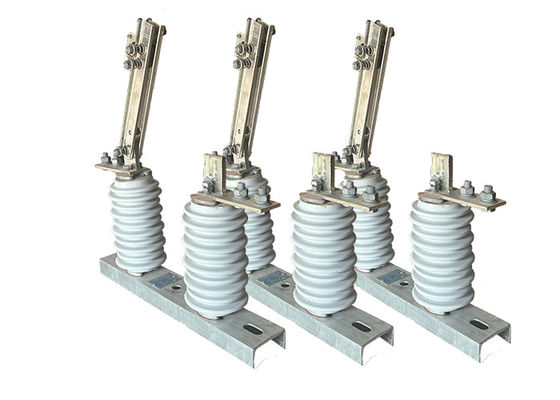
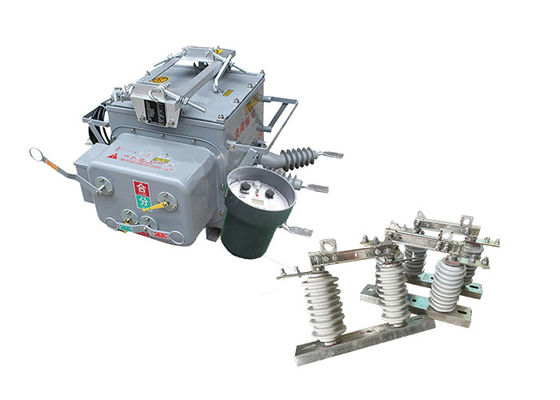
Porcelain Isulator High Voltage Outdoor Disconnector Switch GB 1985-2014 Operated For Electrical Transmission System
Product Decription:
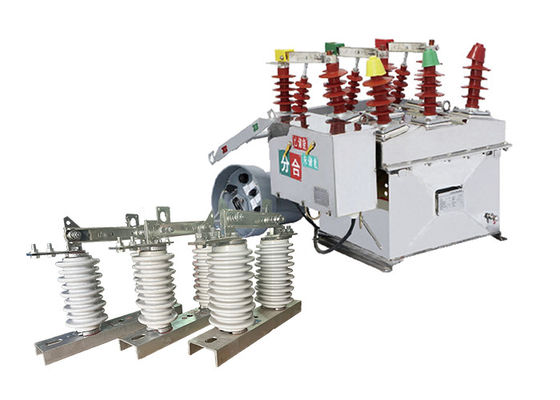
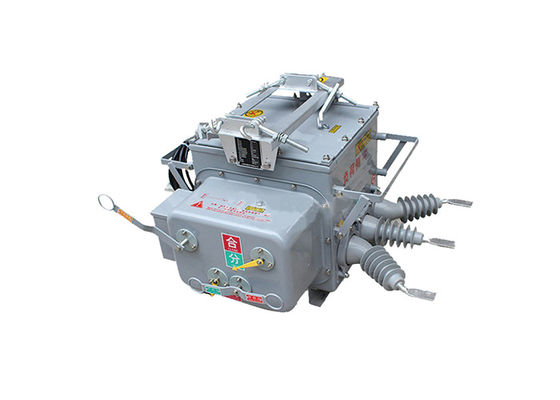
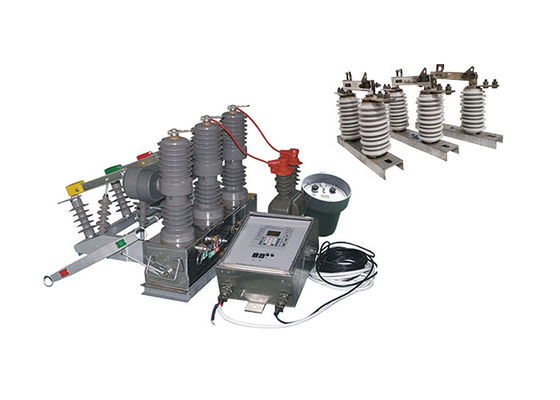
Outdoor disconnector switches are essential components in power transmission and distribution systems, as they allow for the isolation of specific sections of the network for maintenance or repair work. They can also be used to isolate sections of the network in the event of a fault or other abnormal condition.
These switches are designed to handle high voltages and currents, and are typically constructed from durable and robust materials such as stainless steel, aluminum or copper. They are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures, high winds, and heavy rainfall.
There are several types of high voltage disconnect switches, including air-break switches, oil-immersed switches, and gas-insulated switches. Air-break switches are the most common type, and they wor k by using a set of contacts that physically separate when the switch is opened. Oil-immersed switches are typically used in high voltage applications and are filled with oil to prevent arcing when the switch is opened. Gas-insulated switches use sulfur hexafluoride gas to insulate the switch contacts, which allows for smaller and more compact switch designs.
Outdoor disconnector switches must be operated and maintained by qualified personnel who have received proper training. Safety procedures must be followed when working with these switches, including the use of appropriate personal protective equipment and following lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental energization of the equipment. Regular maintenance and testing of high voltage disconnect switches is also important to ensure that they are functioning properly and are safe to use.
Advantage:
1.Simple structure: The isolation switch is designed with a straightforward structure, making it easy to understand and operate.
Low maintenance: Due to its design and construction, the isolation switch requires minimal maintenance, reducing the need for frequent inspections and repairs.
2.High breaking and closing linearity: The isolation switch has excellent breaking and closing linearity, ensuring smooth and reliable operation during switching operations.
3.High reliability: The switch is built to provide dependable performance, minimizing the risk of malfunctions or failures during operation.
4.Comparable to international standards: The GW9-12(W) series isolation switch meets or exceeds the level of similar products both domestically and internationally, ensuring its compatibility and competitiveness in the market.
Safety Tips:
1.Safety interlocks: High voltage disconnect switches may have safety interlock mechanisms that prevent accidental operation or access to the switch while it is energized. These interlocks ensure that the switch can only be operated or accessed when it is in a safe state, reducing the risk of electrical shock or arc flash incidents.
2.Emergency stop buttons: Some high voltage disconnect switches are equipped with emergency stop buttons or switches that can quickly interrupt the power supply in emergency situations. These buttons provide a convenient and immediate means to disconnect the circuit, enhancing safety during critical events.
3.Ground fault protection: High voltage disconnect switches may incorporate ground fault protection mechanisms that detect and interrupt current leakage to the ground. This protection helps prevent electrical shocks and protects personnel and equipment from the hazards associated with ground faults.
4.Insulation coordination: High voltage disconnect switches are designed to ensure proper insulation coordination with other components in the electrical system. This coordination minimizes the risk of insulation breakdown, flashovers, and subsequent equipment failures, enhancing overall system reliability and safety.
5.Safety training and procedures: Organizations that operate high voltage disconnect switches should provide comprehensive safety training to personnel involved in their operation and maintenance. Safety procedures should be established and followed, including protocols for personal protective equipment (PPE) usage, lockout/tagout procedures, and emergency response.
6.Remote monitoring and diagnostics: Some high voltage disconnect switches feature remote monitoring and diagnostics capabilities. This allows for real-time monitoring of switch parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and contact resistance, enabling early detection of potential issues and proactive maintenance to prevent failures and ensure safe operation.
Operation:
1.Interoperability: High voltage disconnect switches are designed to integrate with other components of the electrical system, such as circuit breakers, transformers, or protective relays. This interoperability allows for coordinated operation and protection of the entire system, ensuring reliable and efficient power distribution.
2.Remote monitoring and diagnostics: Some high voltage disconnect switches are equipped with remote monitoring and diagnostics capabilities. These systems enable real-time monitoring of switch parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and contact resistance, allowing for proactive maintenance and troubleshooting to prevent failures and optimize performance.
3.Emergency operation: High voltage disconnect switches may have provisions for emergency operation, such as manual overrides or emergency power supplies. These features ensure that the switch can be operated even in emergency situations, such as power outages or equipment failures, providing an additional layer of reliability and safety.
4.Compliance with standards: High voltage disconnect switches are designed and manufactured to meet industry standards and regulations, ensuring their safety and performance. Compliance with standards such as IEC, ANSI, or NEMA guarantees that the switch has undergone rigorous testing and meets the necessary requirements for operation in high voltage applications.
Application:
1.Circuit Isolation: High voltage isolator switches are used to isolate a section of a high voltage circuit for maintenance, repair, or testing purposes. By opening the switch, the section can be effectively disconnected from the rest of the system, allowing work to be carried out safely.
2.Load Switching: High voltage isolator switches can be used as load switches to control the flow of electrical power in a circuit. They are particularly useful in situations where the load is relatively small and does not require a circuit breaker or fuse.
3.Overhead Line Protection: High voltage isolator switches are often installed on overhead power lines to provide protection against lightning strikes and other electrical disturbances. By isolating a section of the line, the switch can help prevent damage to equipment and reduce the risk of power outages.
4.Transformer Protection: High voltage isolator switches are also used to protect transformers by isolating them from the electrical network in the event of a fault or overload. By opening the switch, the transformer can be disconnected from the network, preventing damage to the transformer and other equipment.
Technical Parameters:
| Serial No. |
Parameter |
Unit |
Data |
| 1 |
Rated Voltage |
kV |
12 |
| 2 |
Rated Current |
Model No. |
(H)GW9-12(W)/630-20 |
A |
630 |
| (H)GW9-12(W)/1000-20 |
1000 |
| (H)GW9-12(W)/1250-31.5 |
1250 |
| 3 |
4s Short-time withstanding current |
Model No. |
(H)GW9-12(W)/630-20 |
kA |
50 |
| (H)GW9-12(W)/1000-20 |
50 |
| (H)GW9-12(W)/1250-31.5 |
80 |
| 4 |
Rated Insulation Level |
Lightning surge withstand voltage(peak) |
Polar-to-Earth
(Positive & Negative) |
kV |
75 |
Interfracture
(Positive & Negative) |
85 |
Industrial frequency withstand voltage
(1 min)
(Effective value) |
Dry Test/Wet Test |
Polar-to-Earth |
42(Dry)
34(Wet) |
| Interfracture |
48(Dry) |
| 48(Dry) |
48(Dry)
40(Wet) |
| 5 |
Main Circuit Resistance |
μ Ω |
630 |
| 1000 |
| 1250 |
| 6 |
Mechanical Life Time |
times |
50 |
| 50 |
80
|









 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!